Occupational Heat Safety Standards in the United States
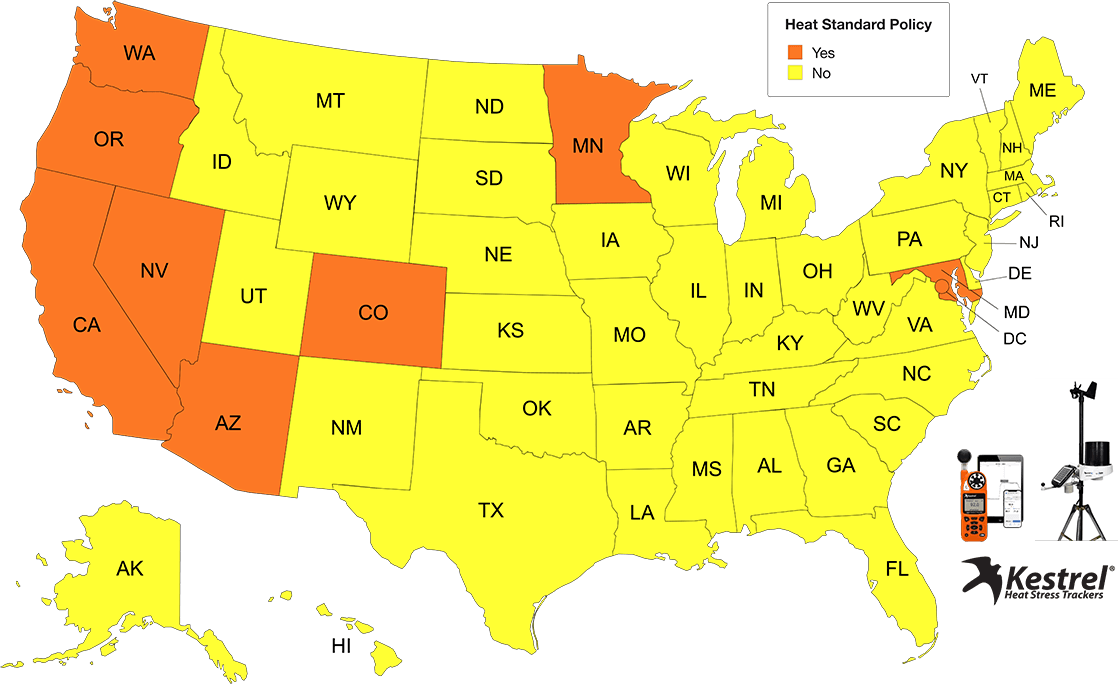
As extreme heat events become more frequent, states are taking action to protect workers from heat-related illnesses.
States with Established Heat Safety Standards
Who is Protected:
Outdoor: Employees and contract workers performing work in an outdoor environment under City contracts.
Thresholds: No specific temperature or WBGT thresholds; protections apply broadly.
Key Requirements:
- Cool drinking water
- Regular breaks
- Access to shaded rest areas and/or air conditioning
- Acclimation practices for newly assigned or reassigned workers
- Heat safety signage
- Annual training with a written Heat Injury and Illness Prevention Safety Plan, Communication, and Emergency Response Protocols
Details/Sources: Phoenix Ordinance G-7241 effective April 2024
Who is Protected:
Indoor & Outdoor: Employees and contract workers at Pima County contract sites where 50% or more of work occurs outdoors, or at indoor locations lacking air conditioning or temperature control.
Thresholds: No specific temperature or WBGT thresholds; protections apply broadly.
Key Requirements:
- Cool drinking water
- Regular breaks
- Access to shaded rest areas and/or air conditioning
- Acclimation practices for newly assigned or reassigned workers
- Heat safety signage
- Annual training with a written Heat Injury and Illness Prevention Safety Plan, Communication, and Emergency Response Protocols
Details/Sources: Pima Ordinance 2024-010 effective September 2024
Who is Protected:
Indoor & Outdoor: All employees working in outdoor environments with high-heat procedures required for the following industries: Agriculture, Construction, Landscaping, Oil and Gas Extraction, and Transportation. Most indoor workplaces where employees wear clothing that restricts heat removal or work in a high-radiant heat area.
Thresholds:
Outdoor Workplaces (Temperature): Shade is required when the temperature exceeds 80°F; high-heat procedures are triggered when the temperature exceeds 95°F.
Indoor Workplaces (Temperature & Heat Index): Preventative measures are required when temperature or heat index reaches or exceeds 87°F. Or if an employee is wearing clothing that restricts heat removal or works in a high radiant heat area and the temperature reaches or exceeds 82°F.
Key Requirements:
Outdoor
- Cool drinking water
- Regular breaks
- Access to shade
Additional High Heat Safety Requirements (above 95°F) include:
- Ensuring effective communication is maintained across the worksite
- Close monitoring & observation of employees for signs of heat illness
- Emergency response plan
- Water break reminders
- Pre-shift safety meetings
- Training on heat illness prevention, hydration, and emergency procedures
- Acclimatization measures are required for new employees and during heat waves
- For Agriculture employees – Minimum 10 min preventative cool down every 2 hours
Indoor
- Access to Cool-Down Areas that are shielded from heat sources
- Implement engineering controls to reduce temperature
- Provide administrative controls like work-rest schedules
- Provide personal heat-protective equipment
- Emergency response plan
- Training on heat illness prevention, hydration, and emergency procedures
- Acclimatization measures are required for new employees and during heat waves
Details/Sources: Ordinance Outdoor: 8 CCR § 3395 effective 2006, Indoor Ordinance 8 CCR § 3396 effective July 2024.
Who is Protected:
Outdoor: Outdoor agricultural workers.
Thresholds:
Temperature: Protections required when temperatures reach or exceed 80°F.
Key Requirements: Employers should follow methods outlined in the Federal Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health 2016 Revised Publication.
- Cool drinking water
- Regular breaks, with additional rest periods for workers engaged in hand weeding, hand thinning, or hand-hot capping
- Access to shade
- Provide protective gear for hand weeding, hand thinning, or hand-hot capping.
- Monitor work/rest schedules
- Acclimatization program for new workers, reassigned workers, and heat waves
- Establish a heat safety prevention plan and emergency response protocols
Details/Sources: Ordinance SB21-087 8-13.5-203 effective October 2021, CDC Occupational Exposure to Heat and Hot Environments
Who is Protected:
Indoor & Outdoor: All employees working in indoor or outdoor environments where the heat index equals or exceeds 80°F.
Thresholds (Heat Index):
Heat Index Equals or Exceeds 80°F: Basic protections required.
Heat Index Equals or Exceeds 90°F: High-heat procedures triggered.
Key Requirements:
- Cool drinking water
- Frequent breaks
- Access to shaded areas and/or mechanical cooling systems.
- Written Heat Illness Prevention and Management Plan that includes emergency response protocols.
- Heat Safety training before initial heat exposure, retraining annually.
- Acclimatization program for new employees or those returning from 7 or more days of absence.
Additional High Heat Safety Requirements:
- Rest periods should be 10 minutes every 2 hours; if above 100°F, rest periods should be 15 minutes every hour.
- Implement an emergency response plan.
Details/Sources: COMAR 09.12.32, effective September 2024
Who is Protected:
Indoor: Indoor manufacturing, warehouse, and industrial facility workers.
Thresholds (WBGT):
WBGT Equals or Exceeds 86°F During Light Work: sitting, standing, or performing light hand or arm work.
WBGT Equals or Exceeds 80°F During Moderate Work: walking about with moderate lifting and pushing.
WBGT Equals or Exceeds 77°F During Heavy Work: heavy lifting and pushing, shovel work.
Key Requirements:
- Minimum air temperature – maintain 60°F air temperature where strenuous work is being performed and 65°F in all other work rooms
- Proper ventilation and circulation of outdoor air
- Maintain a Heat Stress Program
- Engineering Controls to minimize heat load
- Administrative Controls to minimize heat load
- Training on heat stress hazards and prevention
Details/Sources: Ordinance Minn. R. 5205.0110 effective 2024
Who is Protected:
Indoor & Outdoor: All employees working in indoor or outdoor environments where the heat index equals or exceeds 80°F.
Thresholds (WBGT): No specific temperature thresholds; protections are required when a reasonable likelihood of heat illness exists based on:
- Air temperature
- Relative humidity
- Radiant and conductive heat
- Air movement
- Workload intensity and duration
- Protective clothing or PPE
Key Requirements: Employers must complete a one-time job hazard analysis (reviewed upon material changes) to identify heat risks. If risks are present, a written heat illness prevention program must be implemented, including:
- Access to cool water
- Cooling measures
- Rest breaks for affected workers
- Monitoring of work conditions
- Mitigation of heat-generating tasks
- Employee training on heat illness prevention
- Emergency response procedures
Details/Sources: Ordinance R131-24AP effective November 2024.
Who is Protected:
Indoor & Outdoor: All employees working in indoor or outdoor environments where the heat index equals or exceeds 80°F. Exceptions include incidental heat exposures (less than 15 minutes per hour), heat generated solely from work processes (e.g., bakeries), emergency operations directly involved in life or property protection, and buildings with mechanical ventilation maintaining a heat index below 80°F.
Thresholds (Heat Index):
Heat Index Equals or Exceeds 80°F: Basic protections required.
Heat Index Equals or Exceeds 90°F: High-heat practices, including mandatory rest breaks, are required.
Key Requirements:
- Access to water
- Access to shade
- Emergency Medical Plan
- Training on risk factors, controls, and employee rights before exposure, with annual training thereafter
- Engineering controls such as increased ventilation, air cooling, and insulation
- Administrative controls for work/rest schedules, heat illness screening, and acclimatization
Additional High Heat Safety Requirements:
- Implement effective communication systems.
- Regular monitoring for signs of alertness and heat illness.
- A cool-down period of at least 10 minutes is needed for every 2 hours of work.
- Develop and Implement emergency medical and acclimatization plans.
Details/Sources: Ordinance OAR 437-002-0156, effective June 2022.
Who is Protected:
Outdoor: All employees performing work in outdoor environments for more than 15 minutes in any 60-minute period when exposed to outdoor heat.
Thresholds (Temperature):
Non-breathable clothing (e.g., vapor barrier clothing or PPE): Protections apply at outdoor temperatures of 52°F and above.
All other clothing: Protections apply at outdoor temperatures of 80°F and above.
High Heat Procedures: Protections apply at outdoor temperatures of 90°F and above.
Key Requirements:
- Cool drinking water
- Frequent breaks with reminders to rehydrate
- Access to shade or other sufficient means to reduce body temperature
- Emergency Response Procedure
- Acclimatization procedures for new employees, employees with an absence of 7 days or more, and heat waves
- Ensure a copy of the Heat Safety Program is available and written in the Accident Prevention Program (APP).
Additional High Heat Safety Requirements:
- Mandatory rest periods of 10 minutes every 2 hours; if above 100°F, rest periods should be 15 minutes every hour.
- Close observation of employees for heat-related illness.
- Regular communication.
- Mandatory buddy system.
Details/Sources: Washington Administrative Code (WAC) 296-62-095, effective July 2023.
